Hurricane Beryl’s Formation and Movement
Hurricane beryl projected path – Hurricane Beryl emerged from a complex interplay of atmospheric conditions over the warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean. Its genesis can be traced back to a tropical wave that originated off the coast of Africa. This wave carried a surge of moisture and unstable air, providing the necessary ingredients for the development of a tropical cyclone.
As Hurricane Beryl barrels through the Atlantic, its projected path remains uncertain. However, meteorologists are using sophisticated computer models, known as spaghetti models , to predict its potential trajectories. These models simulate the hurricane’s behavior under various atmospheric conditions, providing a range of possible paths.
By studying these models, forecasters can better anticipate the storm’s impact and issue timely warnings to affected areas, ensuring communities have ample time to prepare.
As the wave progressed westward, it encountered favorable conditions for intensification. The warm ocean temperatures, coupled with low wind shear and high atmospheric moisture, allowed the wave to organize into a tropical depression. This depression gradually strengthened into a tropical storm, receiving the name “Beryl.”
Direction of Travel
Hurricane Beryl’s path followed a general west-northwestward direction, guided by the prevailing trade winds. It initially moved over the open Atlantic, gaining strength as it traversed the warm waters. As it approached the Lesser Antilles, Beryl encountered some wind shear, which caused a slight deviation in its trajectory. However, the hurricane maintained its overall direction, continuing its journey towards the Caribbean Sea.
Meteorological Influences
The development and movement of Hurricane Beryl were influenced by several key meteorological factors:
- Warm Ocean Temperatures: The warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean provided the energy source for Beryl’s intensification. Warm ocean temperatures allow for the evaporation of water vapor into the atmosphere, which then condenses and releases heat, fueling the hurricane’s growth.
- Low Wind Shear: Wind shear refers to the difference in wind speed and direction at different altitudes. Low wind shear allows hurricanes to maintain their vertical structure and prevents them from becoming disorganized. In the case of Beryl, the low wind shear contributed to its steady intensification.
- High Atmospheric Moisture: The presence of high atmospheric moisture provided abundant water vapor for Beryl’s development. Water vapor is essential for the formation of clouds and precipitation, which are key components of a hurricane’s structure.
Projected Path and Potential Impact: Hurricane Beryl Projected Path
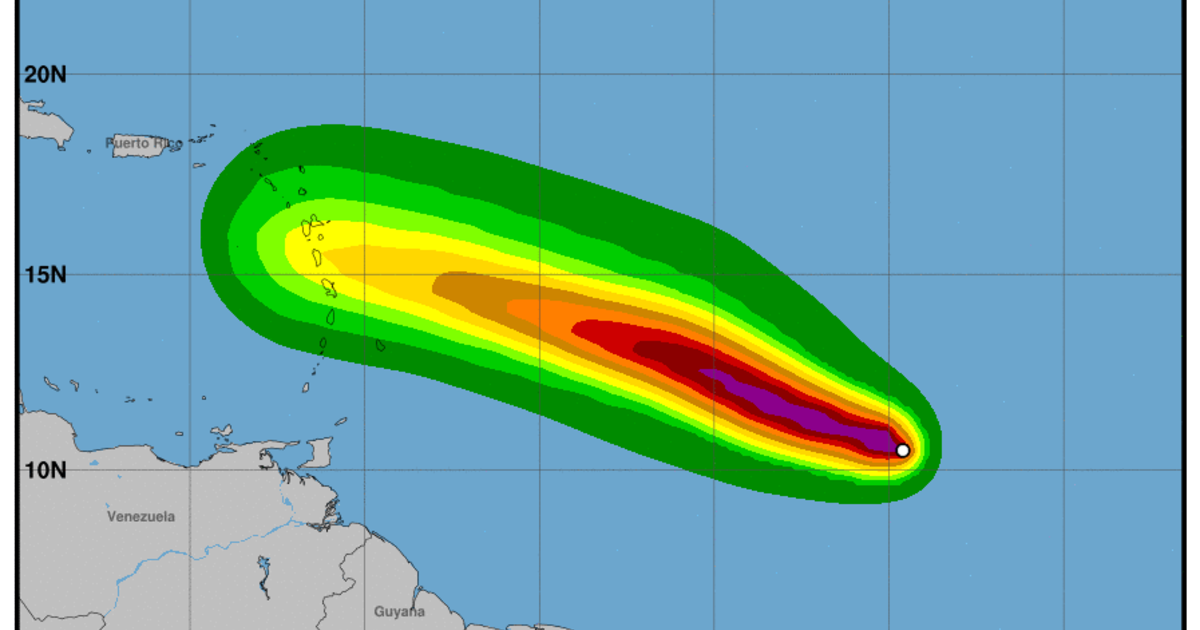
Hurricane Beryl’s projected path is expected to bring significant impacts to coastal areas. Its intensity and trajectory will determine the extent of the damage and the areas most vulnerable to its wrath.
Meteorologists have developed an interactive map that illustrates Hurricane Beryl’s projected path and intensity. This map provides a valuable tool for coastal communities to assess the potential risks and prepare accordingly.
Storm Surge and Flooding
One of the most significant threats posed by Hurricane Beryl is storm surge. Storm surge is a wall of water that is pushed ashore by the force of the hurricane’s winds. It can cause severe flooding and damage to coastal communities.
The height of the storm surge depends on several factors, including the intensity of the hurricane, the shape of the coastline, and the depth of the water. Hurricane Beryl is expected to produce a storm surge of up to 10 feet in some areas.
Storm surge can cause extensive damage to buildings, infrastructure, and ecosystems. It can also lead to loss of life.
Wind Damage
Hurricane Beryl’s high winds can also cause significant damage. Winds of up to 120 miles per hour are expected in some areas.
As Hurricane Beryl’s projected path unfolds, its potential impact on coastal communities looms. Amidst the uncertainty, the resilience of human spirit shines through in the work of individuals like Ian Machado Garry , who dedicate their lives to protecting vulnerable populations.
As Beryl’s course becomes clearer, let us draw inspiration from those who stand ready to face its challenges and ensure the safety of our communities.
High winds can damage buildings, power lines, and trees. They can also create dangerous debris that can injure or kill people.
Vulnerable Populations and Critical Infrastructure
Hurricane Beryl’s projected path is expected to impact several vulnerable populations and critical infrastructure.
Vulnerable populations include the elderly, the young, the poor, and those with disabilities. These populations are more likely to be affected by the hurricane’s impacts and may need assistance in evacuating and recovering.
Critical infrastructure includes hospitals, schools, power plants, and transportation systems. Damage to critical infrastructure can disrupt essential services and make it difficult for communities to recover.
Evacuation Plans and Emergency Response
As Hurricane Beryl approaches, it is crucial for residents in affected areas to heed evacuation plans and follow instructions from local authorities. These plans Artikel designated evacuation routes and shelters to ensure the safety of the population.
Evacuation Procedures
* Monitor official weather updates and advisories to stay informed about the hurricane’s path and intensity.
* Evacuate immediately if instructed by local authorities.
* Gather essential belongings, including medications, important documents, food, and water.
* Secure your home by closing windows and doors, bringing in outdoor furniture, and unplugging electronics.
* Follow designated evacuation routes and avoid flooded areas.
* Stay informed by tuning into local news and emergency broadcasts.
Role of Local Authorities and Emergency Responders
* Local authorities coordinate evacuation plans and provide updates on the hurricane’s progress.
* Emergency responders, including police, firefighters, and medical personnel, are on standby to assist with evacuations, provide aid, and respond to emergencies.
* Emergency shelters are established to provide temporary housing and essential services to evacuees.
Available Resources and Support
* Evacuees may access financial assistance, food, water, and medical care at designated shelters.
* Local organizations and volunteers offer support services, such as transportation and emotional counseling.
* Government agencies provide disaster relief funds and assistance programs for affected individuals and communities.
By following evacuation plans and staying informed, residents can help ensure their safety and the well-being of their community as Hurricane Beryl approaches.
Economic and Environmental Impacts
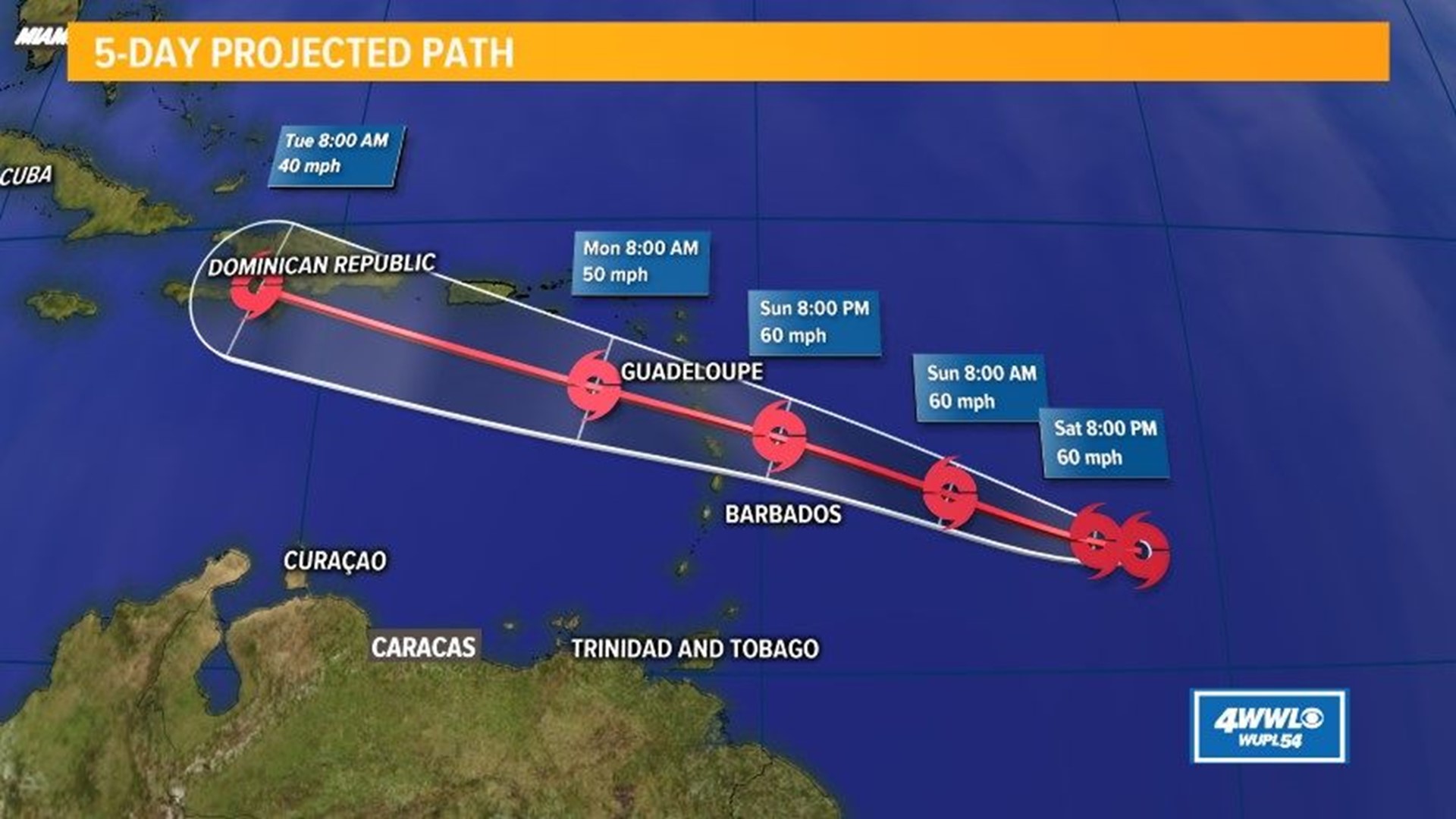
Hurricane Beryl has the potential to cause significant economic and environmental damage. The storm’s high winds and heavy rains can lead to property damage, infrastructure disruption, and business closures.
The economic impact of Hurricane Beryl will depend on the severity of the storm and the areas it affects. However, even a relatively weak hurricane can cause billions of dollars in damage. For example, Hurricane Harvey, which made landfall in Texas in 2017, caused an estimated $125 billion in damage.
Coastal Erosion, Hurricane beryl projected path
Hurricanes can also have a significant impact on the environment. The storm’s high winds and waves can cause coastal erosion, which can damage beaches and dunes. Coastal erosion can also lead to the loss of property and infrastructure.
Flooding
Hurricanes can also cause flooding, which can damage homes, businesses, and infrastructure. Flooding can also contaminate water supplies and lead to the spread of disease.
Disruption of Marine Ecosystems
Hurricanes can also disrupt marine ecosystems. The storm’s high winds and waves can damage coral reefs and seagrass beds. These ecosystems are important for fish and other marine life.
Mitigation Measures
There are a number of measures that can be taken to mitigate the negative impacts of hurricanes. These measures include:
- Building seawalls and levees to protect coastal areas from flooding
- Planting trees and vegetation to help stabilize dunes and reduce erosion
- Educating the public about hurricane preparedness and safety
- Developing emergency response plans
